Conductor of thermal break window glass facade
Conductor of thermal break window glass facade ,In the world of architecture and construction, the pursuit of energy efficiency and sustainability has become paramount. Among the myriad innovations aimed at achieving these goals, thermal break window glass facades have emerged as a standout solution. These facades incorporate a conductor of thermal break technology, which plays a crucial role in enhancing the energy performance of buildings while simultaneously providing aesthetic appeal. Let’s delve into the significance and workings of this essential component.
Understanding Thermal Break Technology
Thermal break technology is a design feature integrated into window and facade systems to minimize thermal conductivity between the interior and exterior components. In essence, it creates a barrier that reduces the transfer of heat or cold through the window frame, thereby enhancing energy efficiency within buildings.
Traditionally, window frames were made of materials like aluminum, which conducts heat relatively well. This meant that during cold weather, heat would escape through the frame, leading to increased energy consumption for heating. Conversely, in hot climates, the frame would transfer heat indoors, necessitating greater energy use for cooling. Thermal break technology addresses these challenges by interrupting the thermal flow, thereby mitigating heat loss or gain.
The Role of Conductors in Thermal Break Facades
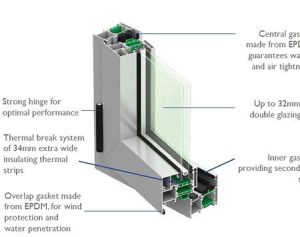
Conductors are at the heart of thermal break window glass facades. They are strategically placed within the frame to disrupt the thermal bridge between the interior and exterior surfaces. These conductors are typically made of materials with low thermal conductivity, such as reinforced polyamide or other composite materials.
The conductor is designed to be inserted between the inner and outer layers of the window frame, effectively creating a break in the thermal pathway. By separating the metal components of the frame, the conductor inhibits the transfer of heat or cold, thereby improving the overall thermal performance of the facade.
Advantages of Thermal Break Window Glass Facades
1. Energy Efficiency:
- By minimizing heat transfer, thermal break facades reduce the reliance on heating and cooling systems, leading to significant energy savings over time.
2. Enhanced Comfort:
- Improved insulation means better temperature control within buildings, creating a more comfortable indoor environment for occupants.
3. Sustainability:
- Reduced energy consumption translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to environmental sustainability and meeting regulatory requirements.
4. Condensation Control:
- Thermal break technology helps prevent condensation from forming on window frames, reducing the risk of moisture-related issues such as mold growth and structural damage.
Applications and Considerations
Thermal break window glass facades find applications across various building types, including commercial offices, residential complexes, educational institutions, and healthcare facilities. Their versatility, coupled with their energy-saving benefits, makes them a preferred choice for modern construction projects.
However, it’s essential to consider several factors when integrating thermal break facades into building designs. These include:
- Material Selection: Choosing high-quality materials for both the conductors and the window panes is crucial to ensuring long-term performance and durability.
- Design Considerations: Proper design and installation are essential to maximizing the effectiveness of thermal break technology. Attention to details such as frame geometry and sealing is paramount.
- Climate Adaptability: Designs should be tailored to suit the specific climate conditions of the location to optimize energy efficiency throughout the year.
- Maintenance Requirements: Regular maintenance is necessary to uphold the performance of thermal break facades and prolong their lifespan.
Challenges and Future Developments
While thermal break window glass facades offer numerous benefits, they are not without challenges. One common concern is the initial cost of implementation, which can be higher compared to traditional window systems. However, it’s essential to view this investment as a long-term strategy that yields significant returns through energy savings and enhanced building performance over the building’s lifespan.
Additionally, the effectiveness of thermal break technology relies on proper installation and maintenance. Inadequate sealing or subpar workmanship can compromise the performance of the facade, leading to thermal inefficiencies and potential issues such as air leakage or water ingress. Therefore, ensuring skilled professionals handle the installation and conducting routine inspections and maintenance are critical steps in maximizing the benefits of thermal break window glass facades.
Looking ahead, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on advancing thermal break technology to further improve its performance and versatility. This includes exploring new materials with even lower thermal conductivity, optimizing frame designs for enhanced insulation, and integrating smart technologies for improved energy management and building automation.
Regulatory Considerations and Industry Standards
As awareness of energy efficiency and environmental sustainability grows, regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing stricter building codes and standards to promote the adoption of green building practices. Many jurisdictions now require buildings to meet specific energy performance criteria, which often include provisions for thermal insulation and fenestration systems.
Industry organizations and certification bodies play a crucial role in establishing guidelines and standards for thermal break window glass facades. Compliance with these standards not only ensures the effectiveness and safety of the facades but also provides assurance to building owners, developers, and occupants regarding their performance and reliability.
The Role of Stakeholders
The successful integration of thermal break window glass facades into building projects requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, manufacturers, and building owners. Each party brings unique expertise and perspectives to the table, contributing to the design, implementation, and ongoing maintenance of the facades.
Architects play a central role in designing buildings that prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability, with thermal break facades as a key component of their designs. Engineers provide technical expertise in optimizing the performance of the facades, ensuring they meet the project’s specific requirements and regulatory standards.
Contractors oversee the installation of thermal break window glass facades, translating design concepts into tangible structures while adhering to quality and safety standards. Manufacturers develop and supply the necessary materials and components, continuously innovating to meet the evolving needs of the industry.
Building owners and developers make critical decisions regarding investment in sustainable building technologies, weighing the upfront costs against long-term benefits. Their commitment to sustainability drives demand for energy-efficient solutions like thermal break window glass facades, ultimately shaping the trajectory of the construction industry towards a greener future.
Economic Implications and Return on Investment
While the initial cost of implementing thermal break window glass facades may be higher compared to conventional window systems, it’s crucial to consider the long-term economic benefits. The energy savings accrued through reduced heating and cooling expenses can lead to significant operational cost reductions over the lifetime of the building. Additionally, improved indoor comfort and environmental performance can enhance the overall value proposition of the property, attracting tenants and commanding higher rental or resale values.
Moreover, governments and municipalities often offer incentives, tax credits, or rebates for adopting energy-efficient building technologies, including thermal break facades. These financial incentives can offset the upfront costs and accelerate the return on investment for building owners and developers.
Aesthetic Considerations and Design Flexibility
Beyond their functional benefits, thermal break window glass facades offer architects and designers considerable flexibility in achieving aesthetic objectives. Advances in manufacturing technologies allow for a wide range of design options, including custom shapes, sizes, and finishes, to complement the architectural style of the building.
Additionally, the use of high-performance glass with low-emissivity coatings further enhances design possibilities by balancing natural daylighting with solar heat gain control. This not only creates visually appealing spaces but also reduces the reliance on artificial lighting and cooling systems, contributing to additional energy savings and environmental benefits.
Social Impact and Occupant Well-being
The implementation of thermal break window glass facades can have a profound impact on occupant well-being and productivity. By providing a comfortable indoor environment with consistent temperatures and ample natural light, these facades create spaces that promote health, productivity, and overall quality of life for building occupants.
Furthermore, the emphasis on sustainability and environmental stewardship resonates with today’s socially conscious consumers and tenants. Buildings equipped with energy-efficient features like thermal break facades demonstrate a commitment to reducing carbon footprints and mitigating climate change, aligning with the values and preferences of environmentally aware individuals and organizations.
Conclusion: Shaping the Future of Building Design
In conclusion, thermal break window glass facades represent a convergence of technological innovation, sustainable design principles, and architectural creativity. As the construction industry continues to evolve towards more energy-efficient and environmentally responsible practices, these facades will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of building design and construction.
By harnessing the power of thermal break technology, architects, engineers, manufacturers, and building owners can create spaces that prioritize energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and environmental sustainability. With careful planning, collaboration, and investment, thermal break window glass facades will continue to pave the way towards a more sustainable, resilient, and aesthetically inspiring built environment for generations to come, Conductor of thermal break window glass facade.





Leave A Comment